Beginners Guide to Sustainable Fabrics for Bags and Fabric Packaging
Here at the Bag Workshop, we have been working hard to make sure that we leave as little impact on the environment as possible, which is incredibly important in the line of manufacturing bags. So, to help you in the right direction to sustainability we have put together a Guide to Sustainable Fabrics – read on to know more.
Choosing products that positively impact the environment, sends a message to your customers. Your commitment to reducing climate change through clever purchasing is the best thing you’ll ever do for the environment and perhaps your customers. It helps them make sensible choices when buying your branded merchandise products because you chose sustainable packaging that won’t cost the earth.
Buying a promotional bag based on its green credentials has a positive impact on several things:
- Demand for better-sourced products.
- Assists manufacturers in solidifying purchasing processes.
- Reduces landfill.
- Reduces carbon emissions.
- Sustainable fabric
Sustainable fabric
What should your sustainable fabric bags be made from? Can eco-friendly packaging that is kind to the environment also look good and be as bling as your brand? This is our Beginners Guide to Sustainable Fabrics that will help you decide which route to take for your sustainable branded merchandise but also ensure a sustainable future for us all.
If you want to make a recycled shopping bag, will it be strong enough and can you wipe it clean? Maybe your customers are demanding a sustainable fabric bag but you’re not sure what that means.
Use this guide to help you decide which sustainable fabric might be best for your custom bag design.
1. Fairtrade cotton
Cotton takes up less than 3% of the world’s farmed land but uses a quarter of the world’s pesticides. As technology and research have improved, safer chemicals have been developed but cost more, so developing countries are still using harmful chemicals to grow cotton which impacts the environment and the health of those involved with the farming.
Fairtrade organic cotton is grown from crops that are not sprayed with pesticides or fertilisers through a process that preserves biodiversity, biological cycles as well as soil health.
Fairtrade certification demonstrates the growing, processing, and manufacturing of the fabric. The certification ensures all elements are compliant and traceable. Our manufacturing facility in India is now certified as a Fairtrade supplier.
With all materials, there are some benefits and disadvantages, let’s take a look:
Benefits of using Fairtrade cotton for promotional bags
- Versatile fabric: This fabric is extremely versatile and is often used to manufacture many different bags and garments alike as it’s available in plenty of different thickness weights to suit your specific needs.
- Lots of design options: Cotton bags can be printed, embroidered, and dyed.
- Ethical sourcing: Fairtrade cotton ensures ethical sourcing practices, providing consumers with the assurance that the cotton used in the bags was produced under fair and just conditions.
- Environmental Responsibility: Fairtrade standards often include environmentally sustainable farming practices. By using Fairtrade cotton, bag manufacturers contribute to the promotion of sustainable agriculture and reduced environmental impact.
- Positive Brand Image: Adopting Fairtrade practices can enhance a brand’s image by demonstrating a commitment to social responsibility and ethical business practices. This can appeal to consumers who prioritise sustainability and ethical sourcing.


Disadvantages of using Fairtrade cotton for bespoke bags
- Higher cost: Fairtrade certification involves additional costs, which may result in higher production costs for bags. This could potentially lead to increased retail prices, making Fairtrade products less competitive in the market.
- Consumer Awareness: Not all consumers may be aware of or prioritize Fairtrade certification when making purchasing decisions. This could limit the market for Fairtrade bags.
- Certification Process: Obtaining and maintaining Fairtrade certification can be a bureaucratic process, and smaller manufacturers may find it challenging to navigate the requirements.
Balancing these factors is crucial for businesses seeking to integrate Fairtrade practices into their manufacturing processes.
2. Recycled cotton
There are two main sources of recycled cotton, including pre-consumer cotton and post-consumer cotton. Pre-consumer, also known as ‘post-manufacturing’, cotton refers to cotton waste generated during the manufacturing process. This is the scrap, offcuts, or defective pieces of fabric.
Post-consumer recycled cotton refers to cotton that comes from products that have been used and discarded by consumers. An example of this would be old clothing, bedding, and cotton-based products that are no longer needed.
Repurposed cotton is produced through a mechanical process and has benefits and challenges. This kind of fabric is a great option to reduce the single use of cotton, but the collection, processing, and shipping of post-consumer waste should be weighed up against the sustainable growth of crops in the first instance. Here are some pros and cons of recycled cotton:
Benefits of recycled cotton for custom bags:
- Versatile fabric: This fabric is extremely versatile and is often used to manufacture many different bags and garments alike as it’s available in plenty of different thickness weights to suit your specific needs.
- Lots of design options: Cotton bags can be printed, embroidered, and dyed.
- Repurposing unwanted textiles: Recycled cotton helps decrease the demand for new raw materials, conserving water, energy, and other resources associated with conventional cotton production and reducing waste products.
- Market Demand: As sustainability becomes a more significant concern for consumers, products made from recycled materials often have a market advantage.
Disadvantages of recycled cotton for custom bags:
- Complex Recycling Process: The recycling process for cotton can be complex and may involve various treatments to remove impurities and prepare the material for reuse, adding to the production costs.
- Awareness and Perception: Some consumers may not fully understand the benefits of recycled cotton or may have concerns about the quality and hygiene of recycled materials.
- Price Fluctuations: The cost of recycled cotton can be more volatile than that of virgin cotton, depending on market dynamics and availability.
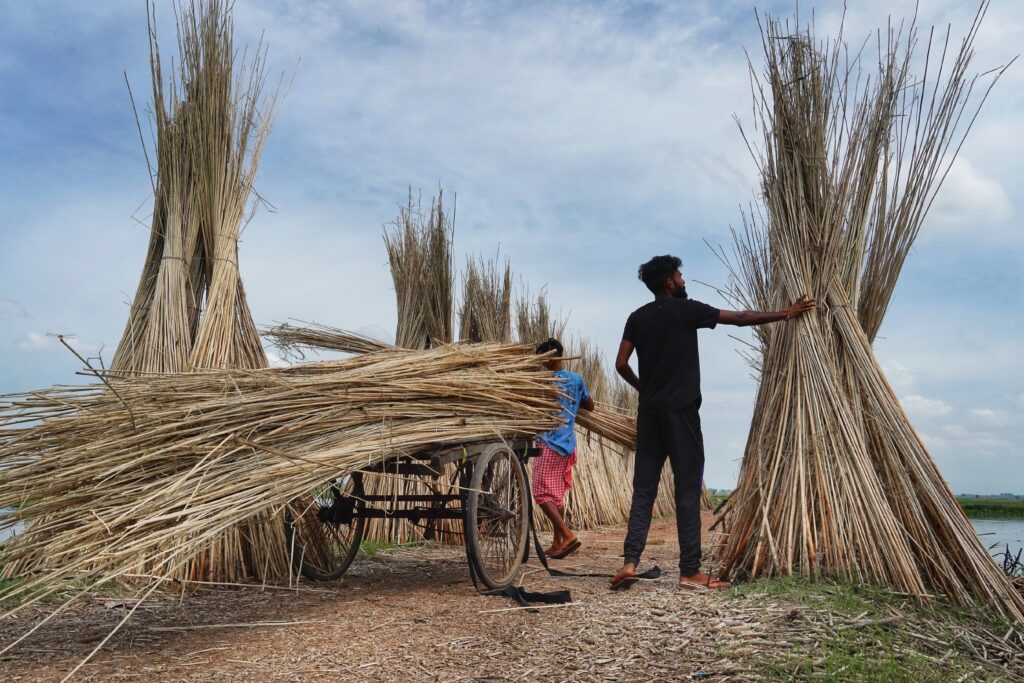
3. Jute bags:
Promotional Jute bags are becoming increasingly popular in the world of bag manufacturing, as an eco-friendly and sustainable fabric alternative to traditional materials such as plastic or synthetic materials.
Jute is a vegetable fiber with superior sustainability compared to cotton. Its cultivation demands less maintenance, fewer pesticides, and fertilisers to yield substantial crops. This remarkable plant exhibits a faster growth and maturation rate, replenishing more swiftly than cotton, and it thrives in smaller cultivation spaces.
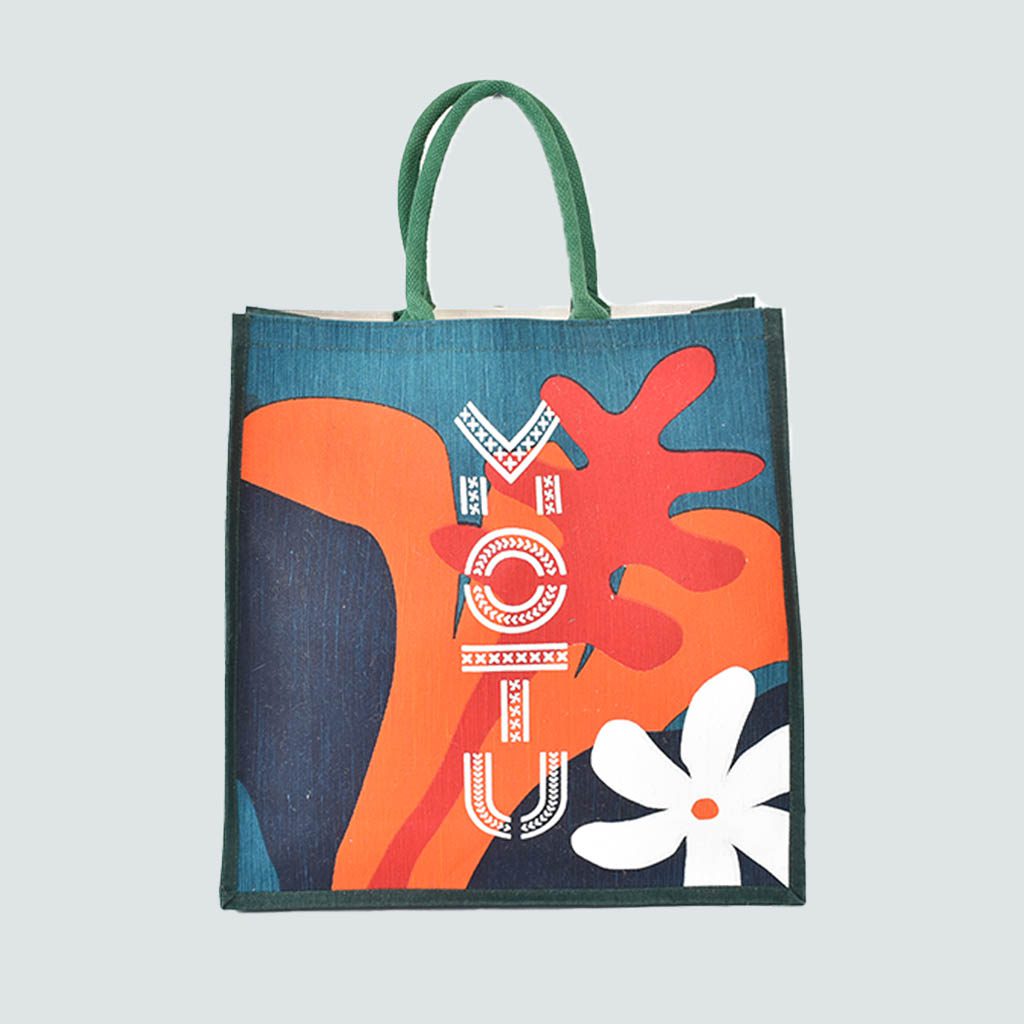



Read on to see the benefits and disadvantages of using Jute as a bag manufacturing material.
Benefits:
- Environmentally Friendly: Jute is a natural fiber that is biodegradable, meaning it can decompose easily without causing environmental harm. This is in contrast to plastic bags, which can persist in the environment for a long time.
- Fast Growth: Jute is a fast-growing crop that requires minimal water and pesticides compared to some other crops, making it a renewable and relatively eco-friendly material.
- Sturdy Material: Jute fibers are robust and durable, making jute bags strong and able to withstand heavy loads. This durability contributes to the longevity of the bags, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Adaptable Material: Jute can be easily blended with other fibers or materials to enhance its properties or appearance. This versatility allows for a range of design options.
- Lower Carbon Emissions: The production of jute typically involves lower carbon emissions compared to the manufacturing of synthetic materials.
Disadvantages of Jute:
- Cultivation Challenges: Jute is primarily grown in specific regions, and the availability of high-quality jute may be limited, affecting the consistent supply of jute bags, if over-sourced.
- Global Supply Chain: The transportation of jute products over long distances can contribute to carbon emissions, especially if they are sourced from regions far from the point of use.
4. RPET
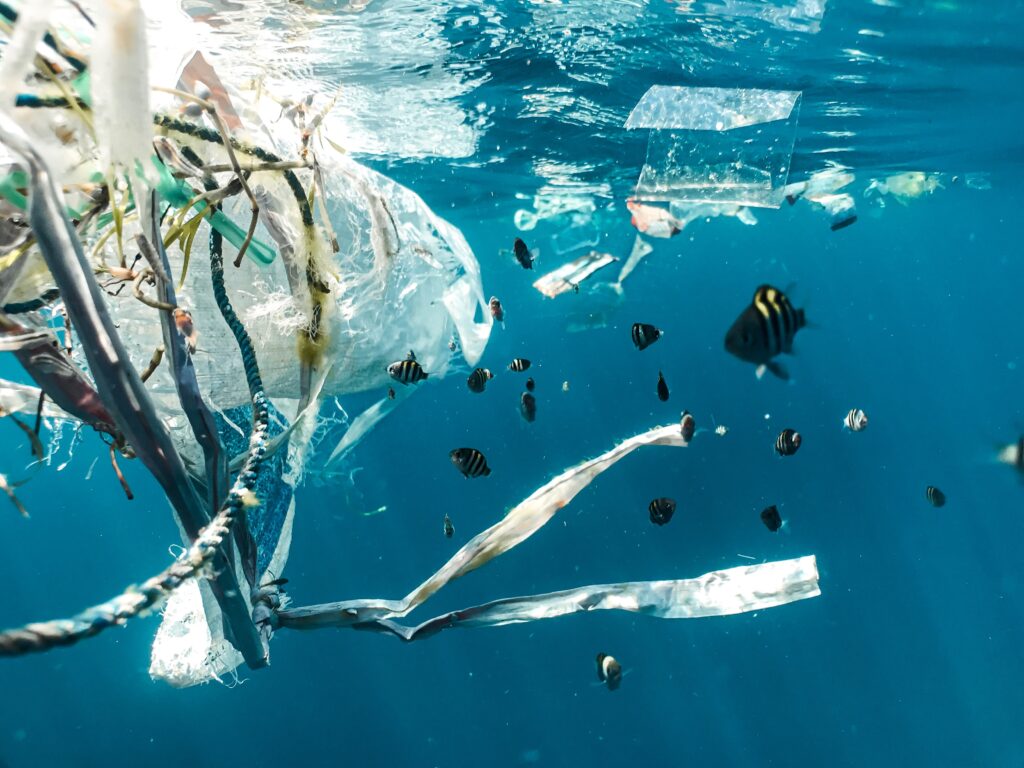
Where possible, we prefer to work with sustainable materials such as RPET, a material often used in manufacturing clothing, bags, and umbrellas, it’s made from recycled PET plastic such as water bottles, reducing the need to manufacture virgin PET plastic.
Here are some pros and cons associated with the use of RPET fabric:
Pros:
- Environmental benefits: RPET fabric is made using recycled plastic bottles, which reduces the need for virgin plastics and therefore reduces the demand for new petroleum-based resources. On top of this, the production of RPET generally uses less energy in comparison to the manufacturing of virgin plastics.
- Reduction of waste: By re-using PET plastics, less material ends up in landfills and the ocean.
- Characteristics: RPET fabric often has very similar characteristics to virgin PET, including durability, moisture-wicking properties (helpful in manufacturing umbrellas), and resistance to wrinkles and abrasion.
- Consumer appeal: Many consumers are increasingly environmentally conscious, and products made from recycled materials may appeal to those seeking more sustainable options.
Cons:
- Chemical processes: The process of recycling plastic bottles and turning them into RPET involves harsh chemical treatments.
- Limited biodegradability: Although RPET is made from recycled plastic, it is not biodegradable itself, so its end-of-life disposal is still a concern. RPET still has a carbon footprint and can release toxins during and after production.
- Energy Use in Processing: While the overall energy use is generally lower than producing virgin polyester, the recycling process for plastic bottles into RPET fabric still requires energy.
- Limited recycling sources: RPET fabric relies on the availability of recycled plastic bottles. If the collection and recycling infrastructure are inadequate, the supply of RPET material may be limited.

5. Tyvek®
Tyvek® is a synthetic substance crafted from densely woven polyethylene fibers. Its remarkable combination of being lightweight, sturdy, and breathable makes it an exceptional material. Additionally, Tyvek® demonstrates resistance to water, abrasion, bacterial intrusion, and the effects of aging. This material finds extensive use in enhancing diverse applications across numerous industries. Tyvek® can be used as a hard structure for industrial packaging and also as a soft structure for customised garments, protective apparel, bags, etc.


However, with all materials, there are benefits and disadvantages. See below:
Benefits of Using Tyvek® as a Sustainable Bag Material:
- Durability: It’s known for its strength and durability, making it resistant to tearing and punctures. This ensures that bags made from Tyvek® can withstand everyday wear and tear.
- Lightweight: Tyvek® is a lightweight material, contributing to the overall portability and comfort of the bags. This is especially beneficial for individuals who prioritize ease of carrying.
- Water Resistance: Exhibits resistance to water, protecting the contents of the bag from light rain or spills. This feature is advantageous for those who need to safeguard their belongings in various weather conditions.
- Recyclability: Aligning with environmentally conscious practices. Bags made from Tyvek® can be recycled at facilities that accept high-density polyethylene (HDPE) materials.
- Breathability: Despite its resistance to water, Tyvek® is breathable. This feature can be beneficial in preventing the buildup of moisture inside the bag, reducing the risk of mould or unpleasant odours.
Disadvantages of using Tyvek®:
- Limited Aesthetic Variety: They often have a distinct appearance that may not suit everyone’s aesthetic preferences. The material may lack the texture and feel of traditional fabrics, limiting design options.
- Perceived Disposable Quality: Tyvek® is often associated with disposable or one-time-use products. Some individuals may perceive these bags as less durable or long-lasting compared to bags made from other materials.
- Cost: Depending on the design and brand, Tyvek® bags may be more expensive than bags made from other materials. The cost can be a consideration for those on a budget.
- Limited insulation: Tyvek® does not provide significant insulation, which may be a drawback for individuals looking to use the bag for transporting temperature-sensitive items.
In closing, the Bag Workshop’s dedication to sustainability is exemplified through our comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Fabrics. Choosing eco-friendly materials for bag manufacturing isn’t just about reducing environmental impact; it’s a commitment that resonates with consumers and contributes to a responsible future. Whether opting for Fairtrade Cotton, Recycled Cotton, Jute, or Tyvek®, each material brings unique advantages and considerations. This guide empowers businesses and consumers alike to make informed decisions, fostering a culture of conscious consumption. By embracing sustainable fabrics, we collectively contribute to a greener, more ethical world—one bag at a time.
To find out more about what we can do, including customised garments, branded umbrellas, and other promotional products, visit our sister companies Wurlin and the Umbrella Workshop for inspiration!